Training assistant early fire extinguishing
1. Definition: Primary fire extinguishing equipment and fire
extinguishing equipment are completely different. The following is shown
separately:
2. Basic fire extinguishing equipment: fire
bucket, fire hook, fire beater, kantha, blanket, all types of portable fire
extinguishers etc.
3. Fire fighting equipment: Pumps / hydrants,
risers, sprinklers, etc. capable of supplying water at a pressure of 6 to 14.
Extinguishing small fires with large fire extinguishers such as pumps, hydrants, etc. will cause more damage to the water than the loss of fire. Reason:
When a large fire is extinguished by a fire bucket / hosiery, the
water in the fire bucket / hosiery will split into the main component (hydrogen
and oxygen) in the excess heat of the big fire and will do more igniting work
instead of extinguishing the fire. Because hydrogen burns and oxygen burns.
Fire (Fire Ignition and Extinguishing Policy)
1. Definition:
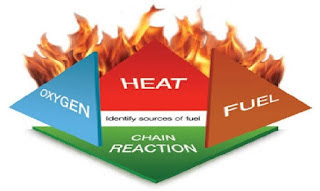
Fire is a non-stop chemical that combines the three elements of
combustion, oxygen and heat (moderate).
An
uninterrupted process of reaction "
2. Fire Ignition Principle: Actually four elements are required for
ignition. These are as follows:
A. Combustible material for combustion.
B. Oxygen.
C. Moderate heat.
D. Non-stop chemical reactions.
Whenever a combination of these four elements occurs, fire originates.
And as long as these four elements are present in the ignition, the fire will
continue to burn. This is the principle of burning fire. Since fire requires
four elements, in modern technology it has been termed as the quadrangle of
fire.
3. Fire Extinguishing Principle: The fire ignition principle states that non-stop
chemical reactions including combustion, moderate heat and oxygen supply are
essential for combustion and the combustion process will continue as long as
these four elements are present in the combustion process. Removing or limiting
any one of these four elements will break the ignition quadrant and the
ignition process will stop, i.e. the fire will be extinguished. This is the
principle of fire fighting. Which has been divided into four parts.
4. Classification of fire: Fire is divided into four categories according to the type of combustible material and to facilitate the use of fire extinguishers:
A. Class- ‘A’. (Solid fire)
B. Class- ‘B’. (Liquid fire)
C. Class- ‘C’. (Fire of gaseous substances)
D. Class- ‘D’. (Metal fire)
Class
‘A’ solid fire is classified as ‘A’ class fire. Being a solid combustible
substance, which has size and volume and so that burning embers are created.
Such as wood, jute, cloth, cotton paper etc. Water is the best extinguishing
medium for ‘A’ class fires.
Extinguishing means:
(1) Water in the form of spray
depending on the type of combustible material.
(2) Water in the form of fog
depending on the type of combustible material
(3) Water in the form of Z
depending on the type of combustible material.
(4) Portable chemical fire extinguishers are
water type, carbon dioxide and dry chemical powder.
(5) Permanent fire extinguishing system of automatic
sprinkler, hydrant, drencher, horsetail etc. according to fire risk.
B. Class-B: Liquid fires are class B-class fires. Such as- petrol,
diesel, octane, kerosene, turpentine, mobile, paint etc. fire.
Extinguishing means:
(1) Water - in the form of
spray.
(2) Mechanical foam.
(3) Chemical foam / air foam.
(4) Carbon dioxide.
(5) Dry chemical powder.
C. Class-C: Fires of gaseous substances belong to the class ‘C’
stage. Such as- L, P gas, methane, propane, butane etc. gas fire.
Extinguishing means:
(1) Shut off gas supply.
(2) Carbon dioxide.
(3) Dry chemical powder.
(4) Water in the form of spray
and jade.
D. Class-D: Metal fire is classified as ‘D’ class fire.
Water in metal fires is ineffective and dangerous. This is because intense heat
can cause water to split into the main component (hydrogen and oxygen) and
cause an explosion.
Extinguishing means:
(1) Graphide powder.
(2) Telecom powder.
(3) Soda Ass.
(4) Lime stone and dry sand.
(5) Special fusing powder,
ternary eutectic chloride and ternary eutectic fluoride.
(6) Sand, ash, asbestos etc.
5. Combustible material: The process by which combustion is done is called
combustible material. Combustibles are one of the four components of ignition.
The need for combustible materials or fuels in the modernization of the modern
world is undeniable. Because daily life is useless without combustible objects.
Apart from this, the need for combustible materials is essential for the
overall development of the country, the movement of vehicles, the operation of
industrial plants and the production of electricity.
Classification
of combustible materials: Modern fire technology divides combustible materials
into three classes according to the differences in density and combustion heat.
6. Classification of Combustible Materials: Combustibles have been divided into three classes according to the differences in density and combustion heat in modern fire technology.
A. Tinder Fuel: This class of combustible material has a very low concentration and is a simple combustible substance. It usually burns at a temperature of 63 degrees Fahrenheit. Such as- petrol, diesel, octane, kerosene, jute, cotton, some chemicals etc.
B. Kindling Fuel: - This class of combustible material has higher density than Tinder fuel and it is medium combustible material It usually burns at 60 to 150 degrees Fahrenheit. Such as- paper, jute, cotton, shola, straw, pieces of thin wood etc.
C. Bulk Fuel: -
Combustibles that normally burn at temperatures above 150 degrees Fahrenheit and
produce burning embers are called bulk fuels. Such as- wood, bamboo, size wood
or round wood etc.
7. Fire Extinguishing Method: The principle of ignition shows that four elements are required to ignite a fire. The fire will be extinguished only if one or more of these four elements can be removed or restricted. Based on this condition, the fire fighting method has been divided into four methods as follows:
A. Method of limiting combustible materials.
B. Oxygen limiting method.
C. Heat limiting method.
D. A method of inhibiting chemical reactions or disconnecting uninterrupted connections.
A. Limiting combustibles There are three ways to limit combustion in firefighting.
(1) By removing flammable material near or around a fire.
(2) By removing fire near or around a combustible object.
(3) By reducing the effectiveness of combustion by dividing the combustible material and hitting small fires with sticks, pulses or beaters.
B. Oxygen limiting method:
Even though the atmosphere is full of oxygen, the fire will be extinguished if oxygen can be stopped from entering the ignited place. Because fire cannot burn without oxygen. It is possible to stop the entry of oxygen by covering the fire with wet Katha, wet blanket etc. Oxygen can be removed or restricted using carbon-di-oxide, foam. However, this method is ineffective in the combustion of flammable objects that can produce oxygen on their own.
C. Heat limiting method
The rate at which heat is generated by combustion is such that if that heat can be limited by various means of extinguishing, then combustion cannot continue. The first step in enforcing this condition of the extinguishing policy would be to quickly remove the excess heat from the fire. The heat absorption capacity of water is immense and water is readily available in our country. That is why water is usually used to limit heat in firefighting. If water is used in fire, it can absorb heat and change into one or more of the following forms:
(1) By absorbing heat, it cools the fire and increases its own heat level.
(2) may evaporate.
(3) can be divided into the main component (hydrogen and oxygen).
(4) may react with flammable combustibles.
Due to the above (1) and (2) changes water can extinguish the fire but (3) it is divided into the main component (hydrogen and oxygen) and helps to light the fire instead of extinguishing it. And (4) can cause danger by reacting with flammable flammable substances.
D. Inhibition of chemical reactions or dissociation of uninterrupted bonding method: - When dry-powder / dry chemical powder is applied on the combustible object during combustion, the powder particle enters the molecule of the ignited combustible material and prevents the vibration of the molecule. As a result, the fire is extinguished by the uninterrupted yoga formula.
8).
The cause of the fire is as follows
A. Stove fire
B. Electrical disturbances or short circuits.
C. Cigarette burning residue.
D. Use of open lights.
E. Boys and girls play with fire.
F. Fireworks or fireworks.
G. Friction of parts.
H. Excessive temperature.
J. Due to lightning.
J. Arson
T. Chimney sparks in industrial boilers
L. Hostile.
M. Sebotage (purpose-induced).
N. Heated ash.
O. Spontaneous ignition.
So. Basically, negligence is the main cause of fire.
9. Fire Remedy:
A. It is imperative to completely turn off the electricity wherever or in any section of the fire the fire signal market immediately. The reason-
(1) If the electricity is on, the electrical insulation may burn out and become a new short circuit and fire may spread to all the factories in a moment.
(2) Exposure to naked wire may result in loss of life of firefighters or ordinary workers.
However, if the sudden stopping of dyeing and finishing during operation can lead to damage to chemicals, yarn, cloth, rubber belts, etc., all other branches except the two mentioned branches have to be switched off immediately after the fire signal market. That branch will have to turn off the electricity.
Responsibilities and duties:
The employees working in the power department will perform this duty.
B. The AC plant must be shut down wherever there is a fire as soon as the fire signal market. Because
(1) If the wind continues to blow, the fire can spread in an instant with the help of flying dust.
(2) The fire with the dust can reach the dust collector and drum filter through ventilation, duct line and can take a deadly shape.
Responsibilities and duties:
(A) The workers working in the AC plant will shut down the AC plant immediately after the fire signal market.
(B) The initial fire brigade team will take special care to prevent any dust including fire from entering the duct line with ventilation as soon as the fire extinguishing work starts, if possible cover the ventilation so that fire cannot enter the dust with ventilation.
(C) In case of fire in any machinery, DCP / CO2 should try to extinguish the fire at the earliest. If there is a possibility of large size fire or spreading, water should be used from the hose.
(D) In case of fire in cloth or any other solid, DCP, CO 2 should be used and water should be used from the hose. If there is a possibility of the fire getting bigger or spreading, the fire should be extinguished with a line from the hydrant.
(E) Fire extinguishing work should always be started keeping in view the progress of the fire.
(F) False sailing can spread rapidly if it comes in contact with fire. If you see the fire getting bigger, you have to soak it with false sealing water before starting the fire.
(G) In case of fire in false ceiling, water should be given by standing next to it without standing directly under the fire.
10.
The process of spreading fire:
In the principle of combustion we have found that fire is started by three elements and a heroic chemical reaction and fire continues as long as the three elements are supplied in the right quantity. And the burning process increases and at one point the fire spreads. The main component of the combustion process is heat, and this heat conducts the expansion of the combustion process. So in the process of spreading fire, heat is transmitted in three ways such as -
A. Transportation.
B. Management.
C. Radiation.
A. Transportation
The process by which the molecules of a substance do not change their own position but simply give a molecule heat to its surrounding molecule through vibration and transfer heat from the warmer part to the cooler part of the matter is called transport.
Example: Holding one end of a metal rod in the fire and holding the other end in the hand makes the hand feel very hot after a while. The molecules of the part of the bar that is in the fire receive heat from the fire and provide heat to the surrounding cold molecules by vibrating from their position. Thus, the transfer of heat from one molecule of a metal to another is called transport.
B. Conduction: The process by which heat is transferred from the warmer part to the colder part by the movement of the molecules of a substance is called conduction. Heat of liquids and gases is conducted in this manner.
Example: When a liquid heats up, it becomes lighter and the lighter liquid rises to the top. Then the surrounding cold liquid occupies that space. In this way, the liquid becomes lighter at higher temperatures and rises in the form of gas through stairs, elevators or door / window spaces, heating the combustible material in that place and catching fire.
C. Radiation: The process by which heat is transmitted from a warm object to a cool object in the form of an electromagnetic wave without the aid of an inert medium is called radiation.
Transport and handling requires a medium for heat to move from one place to another. But heat radiation method does not require medium. In this method heat can be transmitted through the empty space.
Example: The main source of heat energy is the sun. The heat energy radiated from the sun is mainly in the form of "bend of web lens". Which is called light. Because after being caught in the eye. But the heat that is not caught in the retina of the eye radiates in an infrared wave. A substance that reflects without absorbing heat is called a transparent substance, such as glass. In the forest, fire is reflected through the transparent glass and reflects the heat of the sun. This heat enters the room through the window glass, radiates and can catch fire anywhere else in this way.
Portable chemical fire extinguisher
Portable Fire Extinguisher
Topic: Portable chemical fire extinguishers are generally divided into 4 categories based on different types of fire extinguishers.
A. Portable water type fire extinguisher.
B. Portable foam type fire extinguisher.
C. Portable carbon-dioxide fire extinguisher.
D. Portable dry-chemical fire extinguisher.
A. Water type and b. Foam type is not used here.
C. Portable carbon-dioxide fire extinguisher
(1) Definition: A fire extinguisher that easily carries carbon-di-oxide gas and restricts oxygen from the combustible material is called a portable carbon-dioxide fire extinguisher.
(2) Structure: The cylinder of
this device is made of steel. Tested at a pressure of 3,375 pound per square inch.
There is an operating lever on the top of the cylinder. The cylinder has a
handle for carrying gas, a pressure release valve for gas outlet, a hose pipe
with high pressure tolerance, a handle for holding, gas expansion horn, a
discharge tube for gas outlet from the cylinder and a safety pin.
(3) How to use: When used for firefighting, when the horn is aimed at the fire, a safe pin is opened and pressure is released on the pressure lever. Removing will extinguish the fire by creating a snow cover on the combustible object. Discharge wrench is only 3 meters and discharge time is only 5 to 30 seconds.
(4) Benefits:
(A) This gas is non-toxic. This gas does not burn itself, does not help others to burn
(B) Does not react with most substances except metals.
(C) This gas comes out of the cylinder at its own pressure.
(D) This gas is electrically non-conductive and does not cause any damage to sensitive electrical equipment.
(E) The gas is clean so it has no effect on the combustible material.
(F) 1 liter of liquid carbon-di-oxide gas produces about 0.5 cubic meters of free gas. Its spread ratio is 450: 1.
(5) Disadvantages:
(A) The time taken out of the carbon-di-oxide gas cylinder is very short. So failure to take full advantage of this short time will disrupt the purpose. The maximum exhaust time of a 7.8 liter device is only 30 seconds.
(B) Coolburn can occur if the gas comes out of the hand.
(C) If the concentration of this gas in the air is more than 9%, there will be shortness of breath.
(D) Exhaust gas can create dense vapor in a closed room and limit vision.
(E) When used in open space, this gas can be removed by pushing air before extinguishing the fire.
(F) When used in metal fires, this gas can split into the main component and cause an explosion.
(G) The resistivity of this gas is low. Because this gas cannot
completely cool the combustible material.
(6) Refilling and maintenance: If not used in fire, refilling should be done after 10 years. Need to check weight every month. If the weight is less than 10% of the total weight, it has to be re-admitted. Care should be taken to ensure that the horn and flexible hose pipe are not damaged.
D. Portable dry-chemical fire extinguisher
(1) Definition:
A portable dry chemical powder fire extinguisher is a fire extinguisher that can easily extinguish dry chemical powder.
(2) Types: Drychemical fire extinguishers 2 types. -
(A) Stored pressure type.
(B) Gas cartridge type.
(3) Structure: The cylinder of dry chemical fire extinguisher is made of mild steel and is tested at a pressure of 350 pounds per square inch. The mouth of the cylinder is enclosed by a cap. The cap has a lever or trigger and a secure pin attached to it. The gas cartridge type has a tube for exiting the carbon-di-oxide gas cylinder and a discharge tube for the powder to exit through the cylinder. There is only one discharge tube for storing pressure type powder. There is a hose pipe at the head of the discharge tube and a nozzle at the head of the hose pipe.
(4) Rules and Effects of Use: When using this fire extinguisher, its safe pin is opened and when the trigger is pressed, the pyder hose comes out through the pipe and nozzle and falls on the combustible object and prevents chemical reaction of the combustible object By
(5) Testing and maintenance: Three months after receipt from the company should be checked: -
(A) The device should be weighed to see if the amount of pider is correct.
(B) Shake the powder to see if it is frozen.
(C) Weigh the gas cartridge to see if it is less than 10%?
(D) Whether the pressure indicator is correct in pressure type?
(E) Nozzle hose pipes etc. should be kept clean.
(F) Whether there is any erosion inside and outside the device?
(G) According to the standard, after 1/2 year, complete discharge would have to be done: re-admitted after examination.
Dust or dust corner fire.
1. Introduction: In large productive plants fine dust or powder or fiber floats in concentrated form or sometimes in the form of small piles. Such dust particles come in contact with heat, oxygen and explode causing fires.
2. The types of dust explosions are as follows:
A. Dust particles ignite very quickly and can cause a dust explosion.
B. Some dust can ignite at a slow speed and cause an explosion. This ignition is flameless. The intensity of the fire explosion in the dust is higher and ignited faster.
3. Dust clouds
Dust particles are formed in the form of condensed dust clouds which are extremely dangerous. Such clouds come in contact with the wind and cause terrible fires, causing fires in buildings, installations or plants, open spaces, etc., causing loss of life and property.
4. Dust cleaning:
If the dust cloud is regularly removed through doors, windows and vents by applying inert gas or air pressure, it is possible to reduce the risk of dust explosion and damage by freeing the installation from dust.
5. The cause of the dust explosion:
A. During grinding / crushing in the machine, a lot of powder is produced in the mill factory and dust explosion occurs in the machine during dust or powder extraction. The part of the machine where dust accumulates is called a cyclone.
B. These grinding machines are usually enclosed. As a result, a lot of dust is deposited there. During dust extraction, dust or ducts and cyclones are friction or electric wires or peas become overheated and explode causing sparks from static electricity.
C. Dust from coal, rubber and zinc sulphate can cause spontaneous fires.
D. During wartime, if a sharp explosive bomb falls on or near a factory, the dust cloud can explode and catch fire in an instant.
E. The Hazardous factory has some dust that requires little heat to catch fire or explode.
. Preventive Measures: The risk of horrific dust explosion can be reduced as mentioned below.
A. Properly construct and keep the building infrastructure of the installation or factory clean and tidy.
B. The factory grinding and cyclone machines should be well covered so that the dust does not condense and spread everywhere. Adequate vents and inert gas should be provided so that small piles cannot be created by spreading or accumulating dust in the room of the plant building.
C. Where cotton or cottonseed products, jute or jute products are processed and flour, flour, rice, maize, etc. are prepared, there should be fire alarm and detection system and sprinkler system to detect the fire and extinguish it automatically. The fire can be extinguished by taking immediate action.
. The precautionary measures and the means of extinguishing the fire are as follows:
A. During Dust Fire Fighting, firefighters need to know what kind of fire is burning in the dust and what kind of risks there are in this fire.
B. If there is a pile of dust in the fire place, water jet cannot be given. This is because if the dust is ignited at the speed of water, it can cause an explosion. Extinguish the fire by applying light water with spray at low speed.
C. Care should be taken to extinguish the fire by avoiding the dust cloud.
D. Foam, vaporizing liquid and water cannot be used in metal dust fires. Fire should be extinguished with DCP, telcum powder, asbestos powder, dry sand, graphite, ash.
E. In order to extinguish the fire of dust in cartons, drums, open containers etc. which cannot be moved or moved, a flood of water has to be put in the book.
F. High-expansion foam can be used in some dust fires.
Permanent fire extinguishing system
1. Definition: In order to protect one's own property or goods from being caught in a fire, if a person or organization creates a permanent or automatic automatic system according to the risk of fire on his own initiative, it is called permanent fire extinguishing system.
2. Types: Permanent fire extinguishing system is divided into 2 parts. E.g. -
A. Extinguishing means - water.
(1) One unit prevention system.
(2) - Sprinkler arrangement.
(3) Hydrant.
(4) Hozril.
(5) Rising main / stand pipe.
(6) Steam.
(1) One unit prevention system: This system for every 250 square feet. Place 3 buckets of water with a capacity of 9 liters at a specific place. The top of the bucket will be covered in red and the word "fire" will be written in white.
(2) Sprinkler, system: It has been divided into 3 parts. E.g.
(A) Sprinkler: An automatic system for extinguishing fires inside houses, businesses, factories etc.
(B) Drencher: Automatic or automatic measures are taken to prevent the fire from coming from any external source and spreading in the organization.
(C) Water spray system projector: In this system fire can be extinguished by using water in the type of combustible boiler which does not mix with water by attaching special type of sprinkler head. It can be done automatically or automatically.
Sprinkler Principles: All spaces of sprinkler buildings should be equipped with pipelines near the ceiling in such a way that all spaces are protected. Normally 6 sprinkler heads have to be placed 10 feet away in the pipeline. A sprinkler head can scatter water on a 100 square foot floor. Sprinkler pipes have to be placed 18 inches away from the ceiling in a puce building and 12 inches away in a raw room. Gambles are placed outside the building along the pipeline, so that the bell can be rung to warn of a fire when the water is flowing.
Sprinkler Features:
It is indicative of fire.
It sounds.
It attacks fire.
It limits the fire.
(3) Hydrant: From the source of water around the factory area or in the area where the hydrant will be installed for fire fighting, the pipeline is surrounded by the ground under the road. Hydrant points are placed between the long pipelines at 60 m to 160 m depending on the risk. The number of hose pipes that can be taken in the entire area for fire extinguishing by connecting the hose pipe to the hose pipe point should be stored at the hose pipe point. There is always a jockey pump to keep the water pressure in the pipeline and 1 associate and 1 alternative pump to increase the water pressure during work. The water supply is available as soon as the wheel is opened by connecting the delivery hose pipe to the hydrant point as a result of keeping the water pressure in the pipeline with the help of jockey pump and immediately the jockey pump and co-pump as required automatically turn on the water pressure. The hydrant is very useful for extinguishing fires as the pressure and flow of water can be found right after opening the wheel by opening a little 2/1 delivery hose pipe from the hydrant point.
(4) Hozril: Each hozril is 100 feet or 30 meters long. Hozril should be placed in such a number that it reaches the edge of each cell. Like the hydrant, the hosiery has a water supply system. Since the hose pipe is thin and the water pressure is low, water can only be thrown into the fire as desired, so that the surrounding goods are not damaged in the water.
(5) Risingmen / Stand Pipes: Rising is a permanent arrangement of placing a permanently standing pipe in a high rise building with a hose connection for water supply on each floor and a connection for booster pump or fire pump on the ground floor. Rising Main has been divided into two parts. E.g. -
(A) Weight Riser: It is not automatic. This arrangement will be in a building with a height of more than 60 meters. The vertical pipeline is always filled with water. The weight riser is connected to the water main by a control valve. The wet riser is to be placed between the booster pump and the 45 cubic meter reservoir building.
(B) Dry Riser: It is not automatic. Dry risers are commonly used in buildings above 18 m and below 60 m. If necessary, work above by connecting the lower connection path by pump or by providing fire service water supply.
(6) Steam: It is commonly used in ship shells, liquids. Well combustion tanks, dryers, etc. are not to be used in water which causes combustible substances.
B. Extinguishing means other than water
(1) Foam (low / high)
(2) Carbon dioxide.
(3) Vaporizing liquid.
(4) Dry powder.
(5) Inert gas.



















0 Comments